CARBON CYCLE DIAGRAM
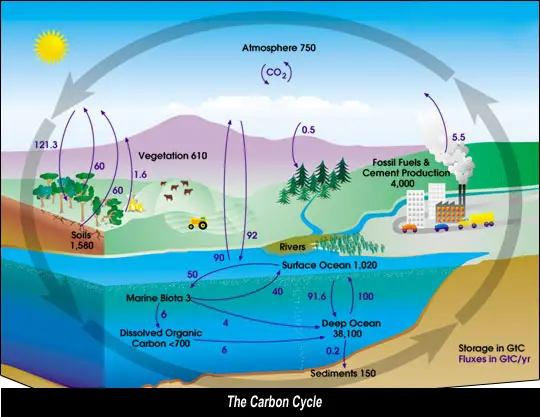
This diagram provides some incite as to where and how carbon is stored in the Earth's system. The Carbon Cycle has four major carbon sinks that exchange amongst one another, these are:
1. the atmosphere
2. the terrestial biosphere which includes fresh water systems and non-living organic material like soil carbon.
3. the oceans
4. the sediments like fossil fuel
Carbon exists in the earth's atmosphere in the form of CO2. There are also other gases in the atmosphere that contain carbon these are methane and chlorofluorocarbons. These gases are known as greenhouse gases and their concentration in our atmosphere is increasing. This increase is contributing to the rise in global surface temperature and lead to excessive global warming because the radioactive forces of CO2 lead to big differences in climate effects.
The way it works...
1. Carbon is initially in the oceans and sedimentary rocks
2. While carbon is in the water it turns into calcium carbonate
3. The algae and coral build up reefs called limestone reefs which cause increased respiration.
4. On land the plants turn the carbon dioxide into carbohydrates through photosynthesis.
5. The carbon is either released into the atmosphere, eaten by animals when plants die, or decomposed into the soil for future consumption by plants and useful resources.
There are action plans in mind such as a concept known as carbon wedges and we can all adopt a 3 step climate change plan and do our share. The fact is that climate changes, the greenhouse effect, and global warming are some of the biggest issues we face in the world today and unless we contribute and do our share to help out we will all pay a high cost later in our futures.
* diagram found on: http://www.globalgreenhousewarming.com/images/CarboncCycleDiagram.jpg
0 comments:
Post a Comment